Interested in learning how to program quantum computers? Then check out our Qiskit textbook Introduction to Quantum Computing with Qiskit.
This tutorial will show you how to create a Random Number Generator in qiskit for IBMs quantum computers.
Implementation
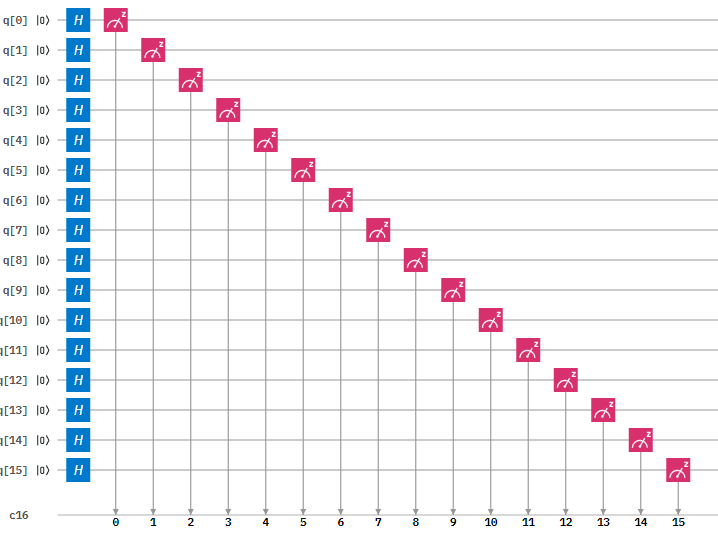
Figure 1: Circuit Diagram of the 16-qubit Random Number Generator
Step 1: Initialise the quantum and classical registers
The first step is to initialise a 16 qubit register . This is done by the following code:
q = QuantumRegister(16,'q')
Next we initialise the 16 bit classical register with the following code:
c = ClassicalRegister(16,'c')
Step 2: Create the circuit
Next we create quantum circuit using the following code:
circuit = QuantumCircuit(q,c)
Step 3: Apply a Hadamard gate to all qubits
Then we need to apply a Hadamard gate. This gate is used to put a qubit in to a superposition of 1 and 0 such that when we measure the qubit it will be 1 or a 0 with equal probability.
This is done with the following code:
circuit.h(q)
Step 4: Measure the qubits
After this we measure the qubits. This measurement will collapse the qubits superposition in to either a 1 or a 0.
This is done with the following code:
circuit.measure(q,c)
How to run the program
Copy and paste the code below in to a python file
Enter your API token in the IBMQ.enable_account('Insert API token here') part
Save and run
Code
from qiskit import QuantumRegister, ClassicalRegister, QuantumCircuit, execute,IBMQ from qiskit.tools.monitor import job_monitor IBMQ.enable_account('ENTER API TOKEN HERE') provider = IBMQ.get_provider(hub='ibm-q') q = QuantumRegister(16,'q') c = ClassicalRegister(16,'c') circuit = QuantumCircuit(q,c) circuit.h(q) # Applies hadamard gate to all qubits circuit.measure(q,c) # Measures all qubits backend = provider.get_backend('ibmq_qasm_simulator') job = execute(circuit, backend, shots=1) print('Executing Job...\n') job_monitor(job) counts = job.result().get_counts() print('RESULT: ',counts,'\n') print('Press any key to close') input()
Output
Once you have ran the program you will get the following output: